3D Printing



What Is 3D Printing?
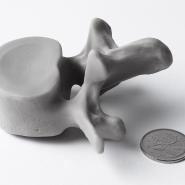
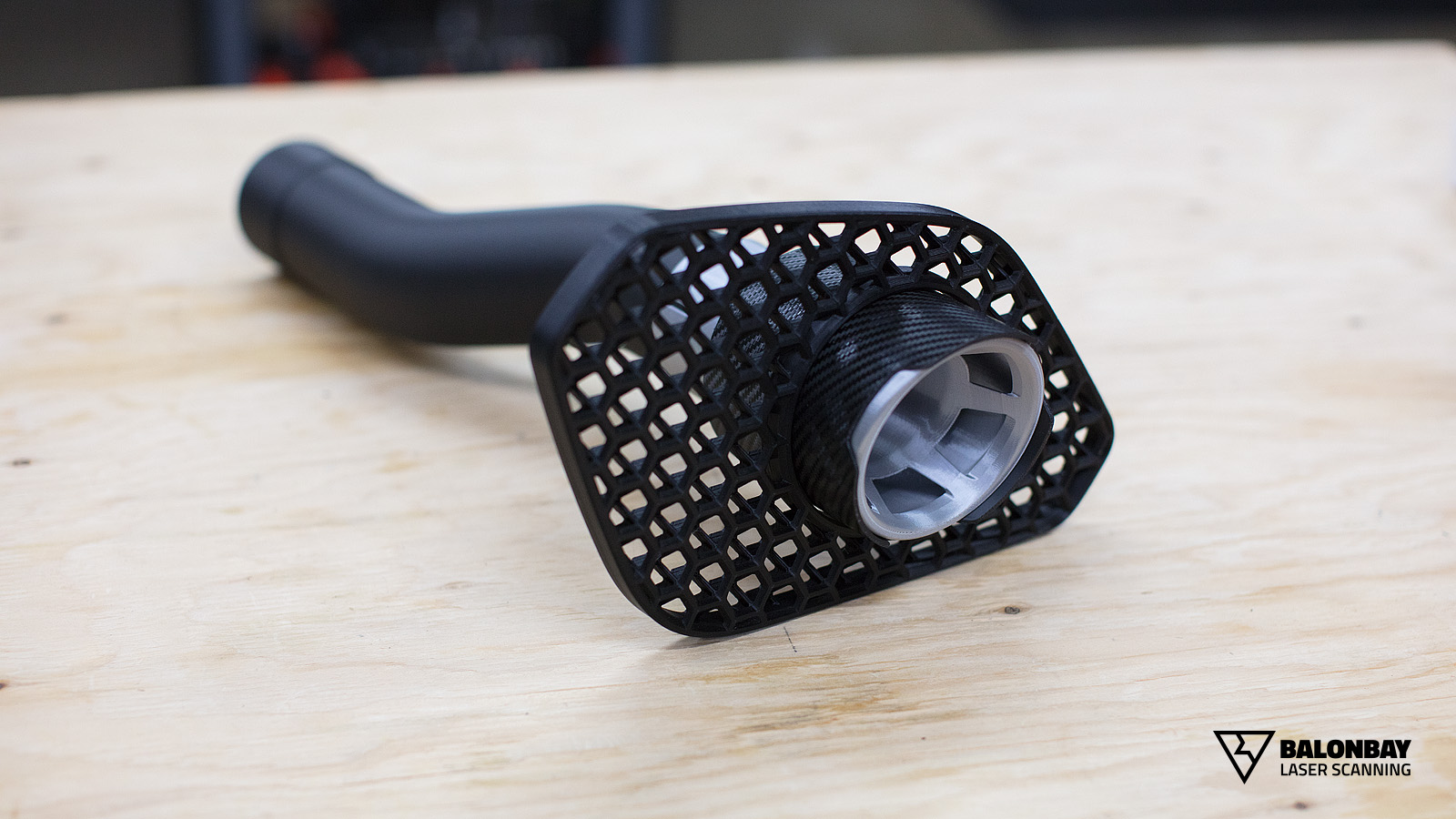
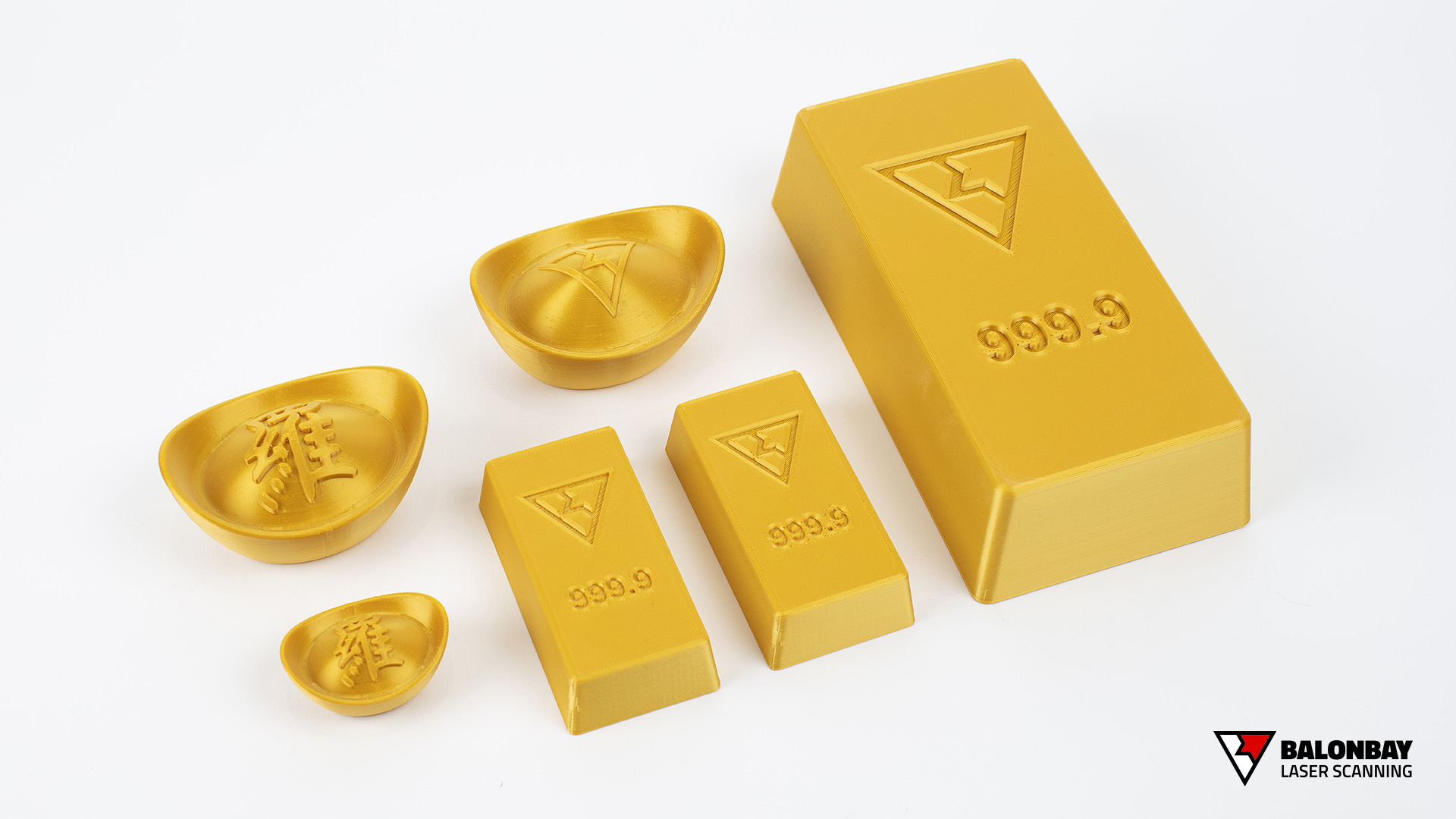
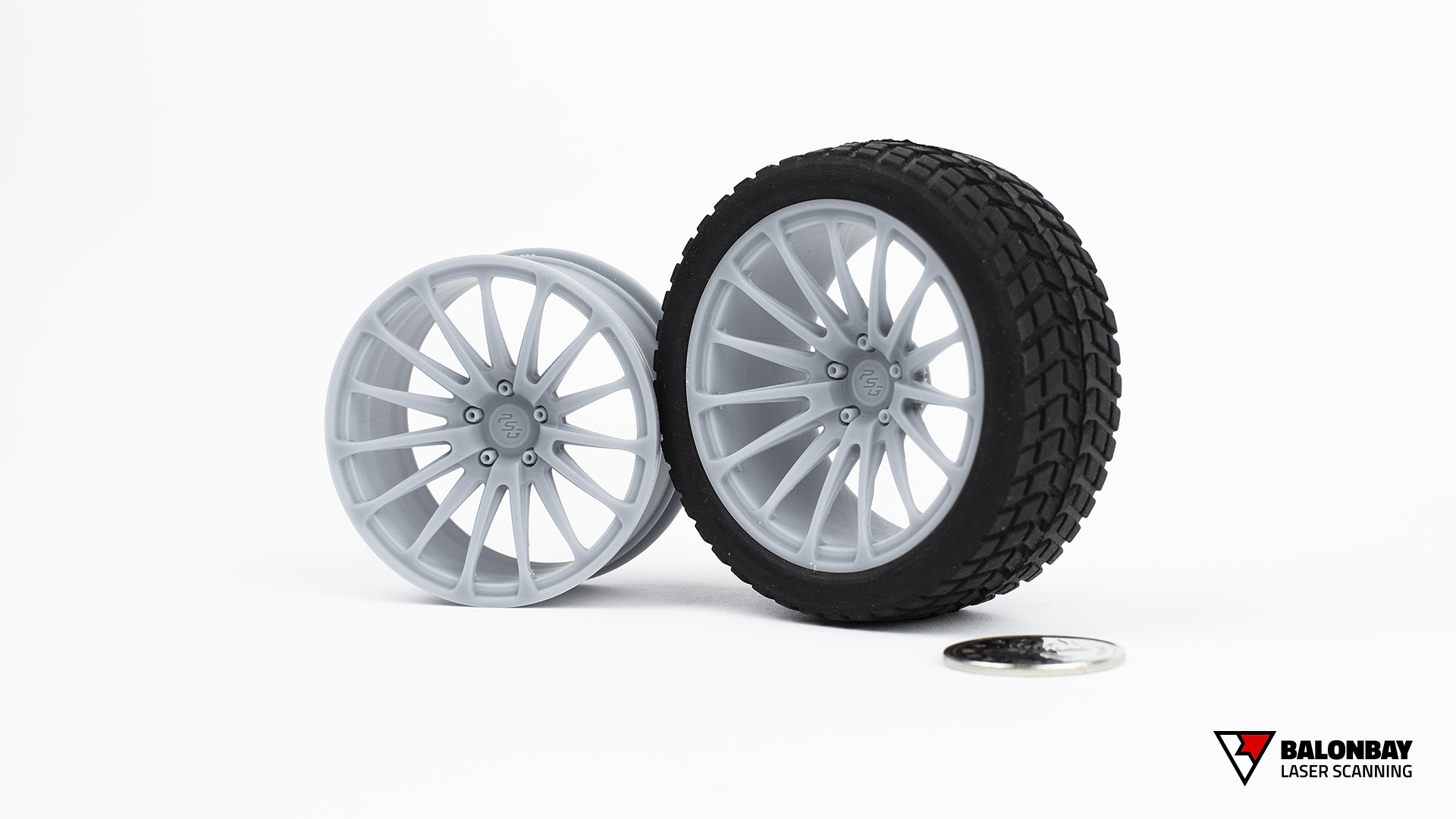
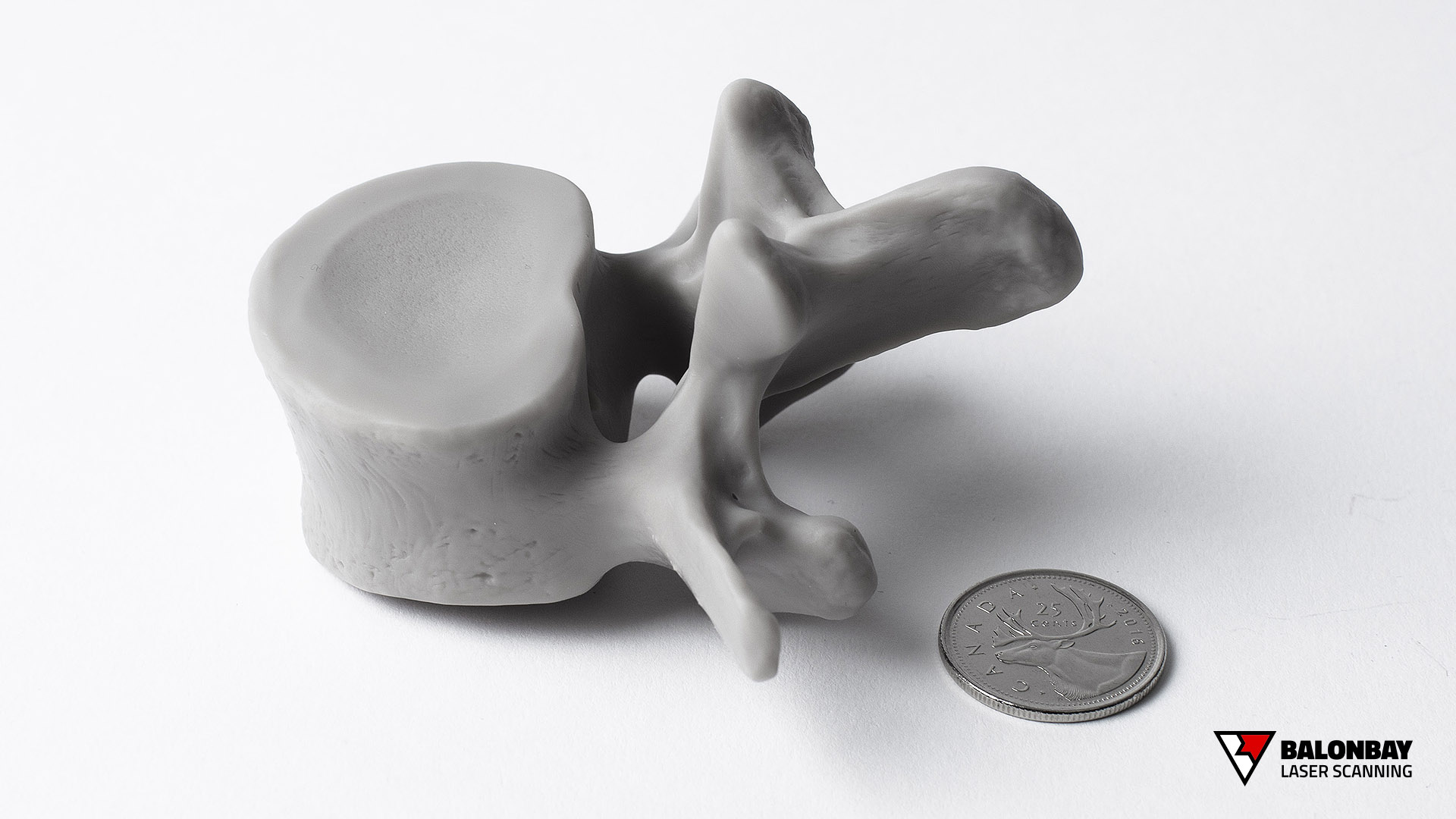
3D Printing (also called Rapid Prototyping) is form of additive manufacturing where the part is built by a machine that continually adds material (as opposed to subtracting). Different types of printers allow for a wide variety of materials, finishes, colours, durability, strength, flexibility, intricacy (details), and usages. However, although the 3D printing processes may differ, they follow the same fundamentals – an object (or multiple objects) is created through a repeating procedure of layer-by-layer build-up of material.
3D printing offers several main advantages over traditional prototyping methods. First, it utilizes material only where necessary, where subtractive manufacturing (CNC milling) requires large supply material and produces a lot of wasted resources. Second, 3D printing allows objects to be created in materials that would normally be difficult or much more costly for low-volume runs – such as polymer plastics. Third, due to the process of layer-by-layer build up, printed models can retain a high level of detail and intricacy.
Technical Information:
| Size and Format: | miniature, small, medium, large, extra-large |
| Materials: | plastic, rubber, resin, hybrid polymer, metal |
| Polymer Processes: | hobby plastic, high temp / strength plastic |
| Liquid Resin Processes: | high detail resin, high-strength resin, rubber |
| Solid Resin Processes: |
multi-colour / multi-material, clear, rubber |
| Powder Processes: |
sintered powder (nylon), Multi-Jet Fusion (HP) |
| Metal Processes: |
sintered (stainless steel, nickel alloy) |
You Need 3D Printing If You:
- need a physical prototype of the design for visualization and development
- need a sample to test-fit or verify measurements
- highly realistic representations and models of the end product (colour, material, etc.)
- strong, durable, functional models to test mechanics (solid plastic, rubbers, etc.)
- are looking for low-volume production (additive manufacturing)
- to make components that are too complicated for traditional methods
Application
3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping is a powerful tool for design development where multiple iterations can be fabricated within a short time frame for optimization and test-fitting. Contact us for all questions regarding processes, materials, and application.